Imperva Advanced Bot Protection detected and stopped the largest bot attack in Imperva history. The web scraping attack targeted a global job listing site with operations in six countries. The attacker used a large-scale botnet, generating no less than 400 million bot requests from nearly 400,000 unique IP addresses over four days with the intent of harvesting job seekers’ profiles. This large-scale attack comes at a time when the Great Resignation continues globally with 44% of Americans and 24% of Brits looking to make a job change. It means that more people will be using job listing sites and uploading their most recent CV in pursuit of their next career opportunity.
What is Web Scraping?
Web Scraping is the use of automated software (also known as bots) to extract content and data from a website. It is considered by the OWASP Foundation as an automated threat (OAT-011), defined as collecting accessible data and/or processed output from the application. While Web Scraping treads a fine line between business intelligence and violating data privacy, it remains one of the most prominent automated attacks affecting organizations today. Scraping can result in lower conversion rates, skewed marketing analytics, decrease in SEO ranking, website latency, and even downtime (usually caused by aggressive scrapers).
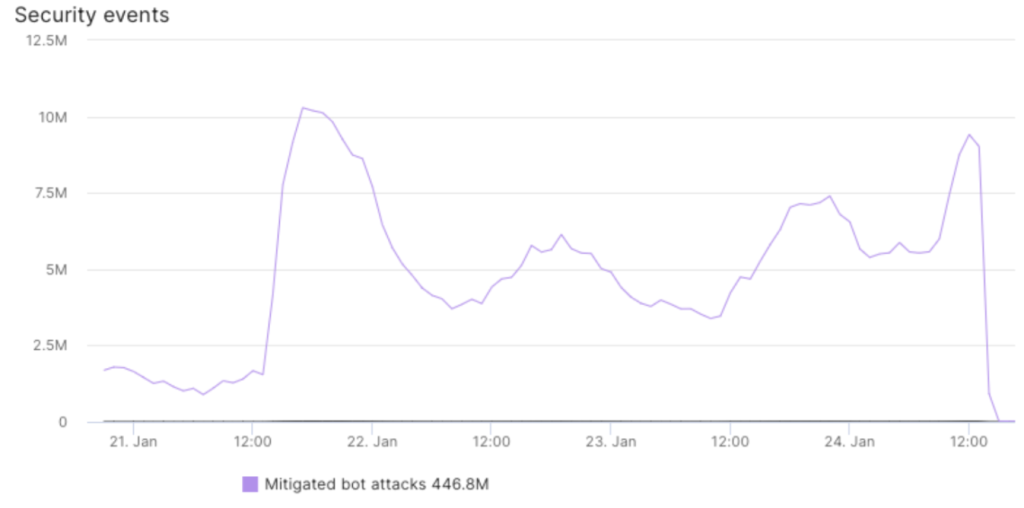
Figure 1: Web scraping bot attacks on targeted site 21-25 January 2022
The large volume of IP addresses used in this particular attack was intended to evade detection. In this situation, each IP was making 10 requests per hour on average. This huge spike represents growth of 30x from regular traffic to this web site which makes it highly unusual. In fact, at some point during the attack, Imperva DDoS Protection also detected the anomalous traffic due to the scale and distributed nature of the attack.
Imperva Advanced Bot Protection does not rely solely on detection through IP addresses, but instead employs a multilayered detection process. This protected the customer from the initial malicious request and throughout the large-scale attack.
Massive bot attacks have become commonplace
During the week of Black Friday 2021, Imperva mitigated a massive scalping attack on a global retailer’s drop of a limited edition collectors’ item. The attack consisted of an astonishing 9 million bot requests to the application in just 15 minutes! For context, that’s 2,500% more than the average web traffic on the retailer’s site.
What is Scalping?
Scalping is defined by the OWASP (OAT-005) as the acquisition of goods or services using the application in a manner that a normal user would be unable to undertake manually (i.e., automation, a.k.a. bots).
Stopping automated bot attacks on hyped, limited-edition product launches ensures that legitimate customers take first priority while leaving scalpers out of the equation. Furthermore, it reduces impact on an organization’s infrastructure from unwanted bot traffic. When websites or applications are overwhelmed by bot traffic, it can result in denial of service, revenue losses, and reputational damage.
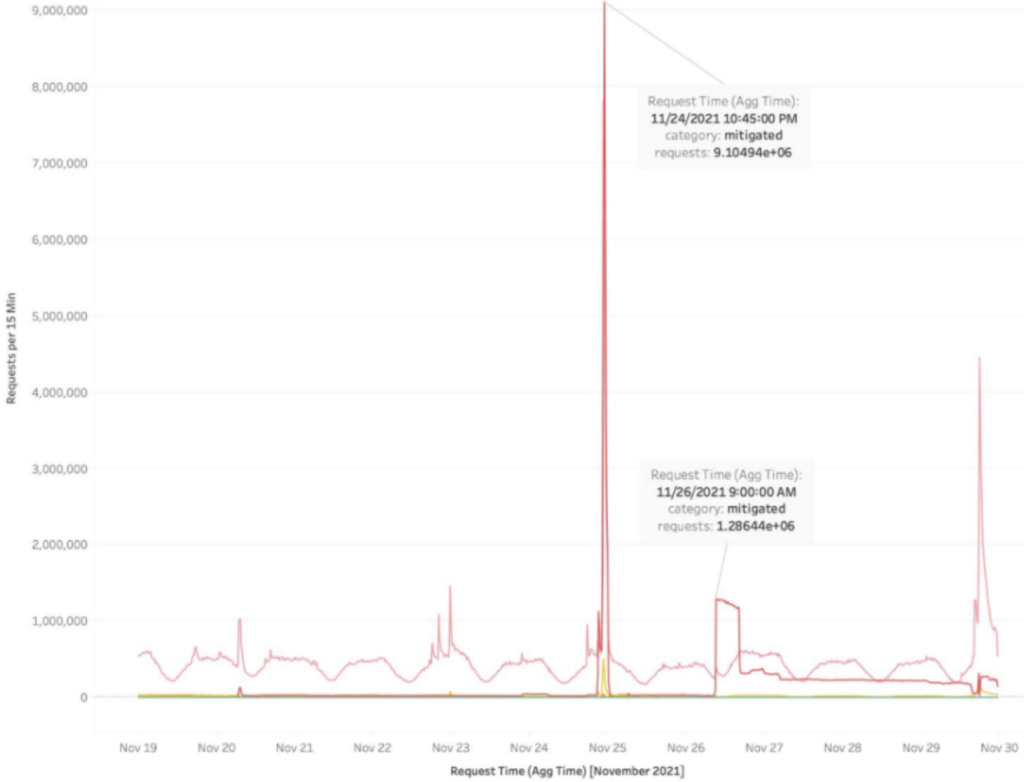
Figure 2: Black Friday 2021 – a short, sharp attack of 9 million bot requests in 15 minutes
This example underscores a growing trend of botnet operators targeting highly anticipated online product launches or “drops”. In 2020, Imperva Research Labs monitored similar levels of traffic around the pre-release of next generation gaming consoles, and again in 2021 around the release of the Nintendo Switch OLED. These launch events generate a lot of online traction, including web traffic and social media chatter. As such, botnet operators seize on the opportunity to scoop up available merchandise before a legitimate consumer can get their hands on it. They then resell the products elsewhere at a significant markup to make a profit.
Adopting a proactive approach
Imperva takes a proactive approach to bot management, rather than a reactive one. Imperva Advanced Bot Protection accurately determines if an interaction with a website has the characteristics of an automated threat through a multilayered process which includes reputational analysis, an advanced client classification engine, and proprietary algorithms. Our machine learning models identify bad bot behavior across all Imperva protected sites, ensuring that customers are protected from the latest threats while stopping bad bots from the initial request.
Prevent online fraud from bad bots with Imperva
As online fraud generated from bot attacks grows in frequency and complexity, organizations are making investments in proper bot management. According to a Google commissioned research conducted by Forrester, 75% of surveyed decision-makers plan to increase their organization’s investment in bot management.
Imperva Advanced Bot Protection is part of the market-leading Imperva Web Application & API Protection (WAAP) solution. It safeguards web applications, mobile apps, and APIs from all automated threats without affecting the flow of business-critical traffic. Our unique, holistic approach provides exceptional service, superior technology, and industry expertise to deliver control over human, good bot, and bad bot traffic.
Advanced Bot Protection is a part of Imperva’s Application Security platform. Start your Application Security Free Trial today to protect your assets from automated threats.
Try Imperva for Free
Protect your business for 30 days on Imperva.